Toothache
Toothaches can be caused by anything from a popcorn husk lodged in the gums to a damaged tooth or bacterial infection. Some toothaches could be caused by transient gum inflammation. You can get more knowledge about some measures to treat as well as how to prevent Tooth pain.
Let’s get started!
What is A Toothache?
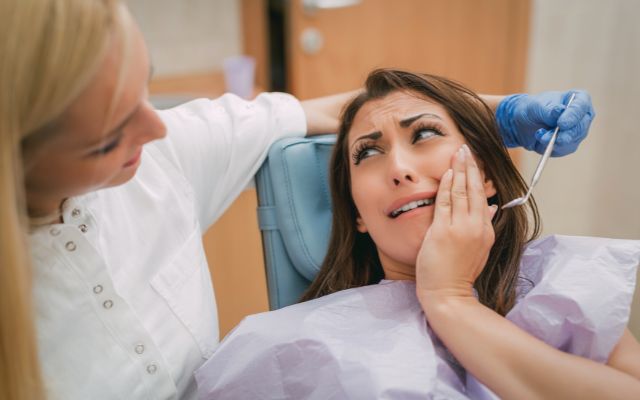

A toothache is discomfort in or around a tooth. Toothaches might be caused by a brief gum irritation that can be treated at home. More severe toothaches are caused by dental and mouth disorders that will not resolve on the
Toothache is a pain in or around a tooth that may be caused by the following:
- Cavity decay
- Infected tooth
- Dental fracture
- A damaged filling
- Repetitive actions, such as chewing gum or grinding teeth, can be harmful.
- Diseased gums, ir own and will require dental treatment.
The pulp within a tooth is a soft substance containing nerves, tissues, and blood vessels. These pulp nerves are among the most delicate in the human body. When these nerves get inflamed or infected with bacteria (abscess), they can produce excruciating pain.
Some Toothache Remedies
Toothaches may be brought on by:
- Dental deterioration.
- Infected tooth (a bacterial infection inside the center of the tooth).
- Dental fracture (broken tooth).
- A defective filling.
- Repetitive actions, such as gum chewing, teeth grinding, or jaw clenching. These actions can
- Cause tooth wear.
- Infected gingiva.
- Eruption (teeth emerging from the gums) or extraction of a tooth (for example, wisdom teeth).
What are Toothache’s Symptoms?
There may be acute, continuous, or throbbing tooth pain. When pressure is placed on the teeth of certain individuals, they experience discomfort (biting down on something).
- Around the tooth swelling.
- Headache and fever.
- The affected tooth exuded foul-tasting discharge.
- The mouth has a foul odor.
- There may be acute, throbbing, or continuous tooth discomfort. Some individuals experience toothache only when pressure is applied.
Call a dentist immediately if you are experiencing difficulty breathing and swallowing in addition to pain.
Ways to Treat Toothache At Home

For temporary toothache relief
- Use warm seawater to rinse. It can also work as a disinfectant and alleviate inflammation. Mix a half teaspoon of salt with a glass of warm water, then thoroughly rinse your mouth, tooth pain, jaw pain, dental pain, clove oil, toothache pain, periodontal abscess, affected area, gum disease, common causes, tooth decay, dental decay, dental problems, sharp pain, essential oil, salt water
- Use hydrogen peroxide to rinse. A 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide reduces inflammation and pain. Dilute the hydrogen peroxide with water in equal parts and thoroughly rinse. Avoid swallowing it.
- An icy compress. For swelling and pain, apply an ice pack wrapped in a towel to the affected area for 20-minute intervals. recurring every few hours
- Medications for the relief of pain. Painkillers available without a prescription help relieve pain and inflammation. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) such as aspirin, ibuprofen (Motrin®, Advil®), and naproxen (Aleve®) can be utilized; if you cannot take NSAIDs, take acetaminophen (Tylenol®). Don’t give aspirin to a child under the age of 16; use Tylenol instead.
Herbal or natural remedies

- Clove oil. A natural antiseptic with analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. Apply a tiny amount of clove oil to the affected region with a cotton swab. Or, add a drop of clove oil to a small glass of water and use it to thoroughly rinse your mouth.
- Vanilla extract. The alcohol in vanilla extract momentarily numbs pain, while its antioxidants promote healing. Several times each day, apply the extract to the tooth and gum using your fingertips or a cotton ball.
- Peppermint tea. With a cooled peppermint tea bag, the analgesic qualities of peppermint can be administered to a hurting location. Place the tea bag against the teeth and gums.
- Garlic. Apply a paste made from a crushed garlic clove to the afflicted area. Garlic can eliminate bacteria (it contains antibacterial allicin) and alleviate pain.
When Should I Seek Dental Treatment for a Toothache?
If any of the following apply, you should see a dentist immediately:
- You have a toothache that persists for more than one or two days.
- Your dental pain is terrible.
- You have a fever, earache, and pain when you open your mouth widely.
It is essential to correctly identify and treat oral infections to prevent their spread to other areas of the face and skull, and even the bloodstream, caries, extraction, trauma, Ludwig’s angina, cavity
The dental team will also perform a physical exam. Your dentist will examine your mouth, teeth, gums, jaws, tongue, throat, sinuses, ears, nose, and neck. To determine the reason for your toothache, X-rays of your mouth will most likely be done.
How Will The Dentist Treat My Toothache?
The treatment administered by a dentist will depend on the cause of your toothache.
- If a cavity is the cause of the toothache, your dentist will treat the cavity or, if required, extract the tooth.
- If an infection of the tooth’s nerve is the cause of the pain, a root canal (a surgery to remove and replace infected pulp with sealing material) may be required. Infection is caused by bacteria that have made their way into the inner space of the tooth’s root.
- If there is fever and jaw swelling, an antibiotic may be administered. A small food particle (such as a popcorn husk) can become lodged under the gums and cause an infection. In this case, a deep cleaning may be performed or advised, followed, if necessary, by additional periodontal (gum) therapy.
Preventions for Toothache Pain Relief
Since the majority of toothaches are caused by tooth decay, excellent dental hygiene can prevent toothaches:
- Brush your teeth with fluoride toothpaste daily.
- At least once every day, floss.
- Twice yearly dental cleanings are recommended.
Additionally, consume low-sugar foods and consult your dentist about sealants and fluoride applications.
Toothache Urgent Care Dentist Near Me
Even though effective preventive care can aid in preventing certain tooth disorders, dental emergencies can occasionally occur. Time is of the essence in dental crises in order to prevent damage, as dental trauma is extremely dangerous.
Certain emergency departments and urgent care dentistry clinics are open 24 hours a day, seven days a week to serve patients with urgent needs.
A toothache can be caused by anything from a popcorn husk lodged in the gums to a cracked tooth or bacterial infection. Some toothaches can be caused by transient gum inflammation. However, severe toothaches must be treated by a dentist in order to alleviate the pain and address the underlying cause.
The emergency dentists at Spring Orchid Dental Emergency Clinic in Bassendean can aid with dental emergencies and other oral health issues.
FAQs
What Stage Of Toothache is Serious?
Visit your dentist as soon as you can to get it treated if your toothache lasts longer than one or two days. It will get worse the longer you wait. The pulp inside your tooth will eventually become infected if your toothache is not addressed.
What Happens If You Don't Treat A Toothache?
Untreated tooth infections can eventually result in blood poisoning, also known as bacteremia or septicemia, or bacteria entering the circulation. If untreated, septicemia can result in sepsis, a serious, perhaps fatal whole-body infection.
How Can A Toothache Affect The Brain?
A tooth abscess increases your risk of developing meningitis. Inflammation of the membranes close to the spinal cord and brain causes this potentially fatal illness. Your brain and spinal cord could be encircled by this bacterial infection if it enters the bloodstream. Meningitis may necessitate lengthy hospital stays.
Can Toothache Make Me ill Or Possibly Kill me?
Toothache alone is not fatal. However, an infection in your tooth (or any other area of your body) that is left untreated might spread. You can become ill, and this disease could become serious or even life-threatening. Therefore, it is advisable to contact your dentist if your toothache does not improve.





