Dental Abscesses: Symptoms, Causes & Treatments Guide
A dental abscess is an accumulation of pus that can develop inside the teeth, in the gums, or in the bone that supports the teeth, and a tooth abscess that is located at the tip of the tooth. The abscess of the gums is referred to as periodontal abscess. In this article, you will learn about the Symptoms, Cause, and Treatment of Dental Abscesses.
Let’s get started!
Overview of Dental Abscess
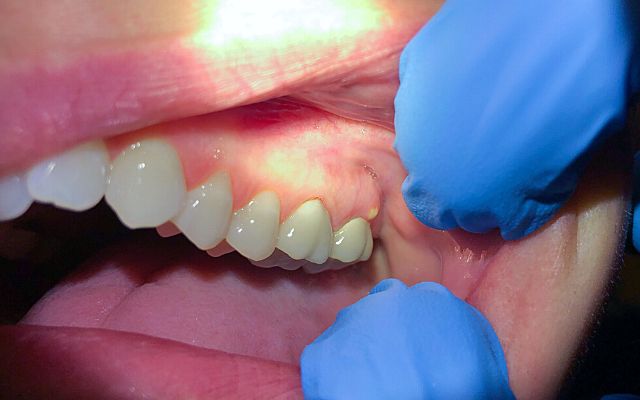
A dental abscess, also known as a Gum abscess, is an accumulation of pus within the teeth or gums. Typically, the abscess is caused by a bacterial infection that has developed in the pulp of the tooth.
Plaque, a byproduct of food, saliva, and germs in the mouth, contains bacteria and adheres to the teeth and gums, causing harm to both. If the plaque is not eliminated by brushing and flossing regularly and properly, the germs may spread into the soft tissue of the tooth or gums. This can ultimately lead to an abscess.
Quick and dirty on tooth abscess swelling:
- There are three types of dental abscesses, including gingival, periodontal, and periapical.
- Pain, a bad taste in the mouth, and fever are all symptoms of dental abscesses.
- An infection with bacteria causes dental abscesses.
- Root canal therapy may be used to treat an abscess.
- Avoid cold beverages and foods and use a softer toothbrush to minimize pain.
What are Symptoms of Dental Abscess?
Once a cavity reaches the dentin, your tooth will likely become much more sensitive. When you chew, you may experience an “off” sensation. When flossing around a tooth with a cavity between teeth, periodontal abscess will often become entangled. Whenever you bite down, there is also a high risk of tooth fracture in mouth infection.
Here some symptoms about Gum Abscess include two stages: Early and Late Tooth
- Sensitivity
- Toothache
- Caries, chipped teeth, and gum disease
- Your dental X-ray reveals a swollen nerve.
- A darkening around the tooth’s root
- A foul taste in the mouth
- Visible pus draining from one or more of your teeth.
- The tooth moves in response to pressure.
- Discoloration of your teeth
- A fistula on the gums adjacent to the tooth root.
- Reddened or swollen gum tissues in that area
In the event that the infection spreads, you may also develop a high temperature (fever) and feel generally ill. In severe cases, you may find it difficult to fully open your mouth and experience difficulty swallowing and breathing and cavities
Some types of Swelling Abscess Tooth
Three types of dental abscesses exist:
- Gingival abscess: The abscess does not harm the tooth or periodontal ligament.
- Periodontal abscess: This abscess begins in the tooth-supporting bone structures.
- Gingival abscess: This abscess begins within the delicate pulp of the tooth.
The severity and location of symptoms will depend on the type of abscess.
Complications of Dental abscess
In the overwhelming majority of instances, complications only arise if the abscess is left untreated. However, complications are extremely uncommon, even after a treatment that appears to be effective. Among the possible complications are:
Tooth cysts
If the abscess is not treated, a fluid-filled cavity may develop at the bottom of the root of the tooth. It is known as a dental cyst. Significant risk exists for the cyst to get infected. If this occurs, the patient may require antibiotics and surgery and dental health
Osteomyelitis
The abscess’ bacteria enter the bloodstream and infect the bone. The patient will have a high body temperature, intense bone pain, and possibly nausea.
Typically, the afflicted bone is close to the abscess site.
As the disease may have gone to the bloodstream, however, any bone in the body may be impacted. Antibiotics may be administered orally or intravenously for treatment.
Sinus cavernous thrombosis
A blood clot forms at the cavernous sinus, a major vein at the base of the brain, due to the spread of bacteria. Cavernous sinus thrombosis is treated with antibiotics and, occasionally, sinus drainage surgery. In some instances, the disease might be fatal. This is an uncommon complication.
Sinusitis of the maxillary sinuses
The germs migrated into the maxillary sinuses, which are tiny areas behind the cheekbones. This ailment is not life-threatening but can be painful. The individual may develop a fever and sore cheeks tooth decay
What Causes Dental Abscess?
Your mouth is full of bacteria, which form a sticky film called plaque on your teeth. The acids produced by the bacteria in plaque can cause tooth decay and gum disease if you don’t keep your teeth clean.

These factors can increase the likelihood of developing a dental abscess:
- Periapical abscess: Typically, a cavity allows bacteria to enter the dental pulp. The pulp is the inner, softer portion of a tooth. Nerves, connective tissue, and blood vessels compose this structure.
- Periodontal abscess: Usually caused by gum disease but can also be the result of an injury.
- Gingival abscess: A foreign object, such as a kernel of popcorn or toothbrush bristle, becomes lodged in the gums.
Additionally, a previous injury or surgery to your teeth or gums – Those with a weakened immune system, such as those suffering from diabetes or taking steroid medication or chemotherapy, are susceptible to bacterial infection of damaged teeth and gums.
This visit is considered mental health services since it can help boost your mood as your smile becomes more attractive and your chewing function improves, making your daily life easier than experiencing previous dental issues.
Ways to present Dental Abscess
You can reduce your risk of developing dental abscesses by maintaining healthy teeth and gums.
To achieve this, you must:
- Use floss or an interdental brush at least once per day to clean between your teeth and below the gum line.
- Brush your teeth twice per day with fluoride toothpaste. Spend at least two minutes per session brushing and avoid rinsing your mouth with water or mouthwash afterward, as this removes the protective toothpaste – Just spit out excess toothpaste and reduce your intake of sugary and starchy foods and beverages.
- Visit your dentist frequently, particularly between meals and before bedtime; your dentist can recommend how often you should have a checkup based on your oral health.
Treatments for Tooth Abscess Swelling
How can a tooth abscess be treated? Depending on the type and severity of your dental abscess, you will require one of the following treatments:
- Endodontic Treatment: If you have an abscessed nerve, root canal therapy is usually your only option. In essence, the nerve is removed, the canal is cleaned, and then the chamber is sealed to avoid reinfection.
Simply covering the tooth with a filling or crown will not solve the problem; it will only trap the infection within the tooth extraction.
- Scaling and root thinning: In periodontal (gum) abscesses, the infection is located in the gums or bone next to the tooth, not the tooth nerve. When this occurs, we must eliminate the bacteria causing the infection. Typically, tartar and plaque are embedded deep under the gums adjacent to the tooth. In such cases, a “deep cleaning” is recommended.
- Dental Extraction: In extreme cases where the tooth abscess is engulfing the tooth and it is impossible to save the tooth, tooth extraction may be the only treatment option. Shortly thereafter, you will also need to devise a way to replace the tooth.
Additionally, if you are unable to see your dentist immediately, you can take an anti-inflammatory medication such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) for pain relief. Warm saltwater gargles may also prove beneficial.
Furthermore, Baking soda, Oregano essential oil, Cold compress, Fenugreek tea, Clove essential oil
If left untreated, an abscessed tooth is a serious infection that could spread to the face and eyes.
If you have a tooth abscess, you should see a physician and a dentist as soon as possible. The remedies listed above are intended to complement the medical treatments prescribed by a physician. You may require antibiotics and dental care immediately.
FAQs
Do Dental Abscesses Need To Be Drained Every Time?
It is crucial to keep in mind that a tooth abscess requires draining in order to be treated. Although most dental abscesses hurt, others can be painless. In any case, it is essential to see an endodontist and have the abscess medically drained.
When Does An Abscessed Tooth Become Serious?
If you have a fever and facial swelling and cannot reach your dentist, visit the emergency department. If you have difficulty breathing or swallowing, you should go visit the emergency hospital. These symptoms may suggest that the infection has gone deeper into the jaw, throat, and neck, or even to other parts of the body.
Can An Abscessed Tooth Persist For Years?
Similarly, maintaining good oral hygiene is essential for preventing unpleasant disorders such as abscesses in the first place. However, we must emphasize that untreated dental abscesses can remain for months or even years.
In Conclusion
Abscessed teeth are an urgent dental emergency. If you have a dental abscess, you must seek emergency care. Abscesses, if left untreated, can result in the spread of infection throughout the body, which can have severe and even fatal consequences. The earlier these problems are addressed, the better!





