A dead tooth, also known as a necrotic tooth, is a tooth that has lost its blood supply and nerve function. Both dental decay and trauma can result in a tooth’s demise. Knowing the causes and symptoms of a dead tooth is critical for maintaining good oral health and avoiding the progression of serious oral problems.
Read on to know more about dead teeth and why it’s imperative to get treatment as soon as possible if you suspect you may have one.
Dead Tooth Meaning
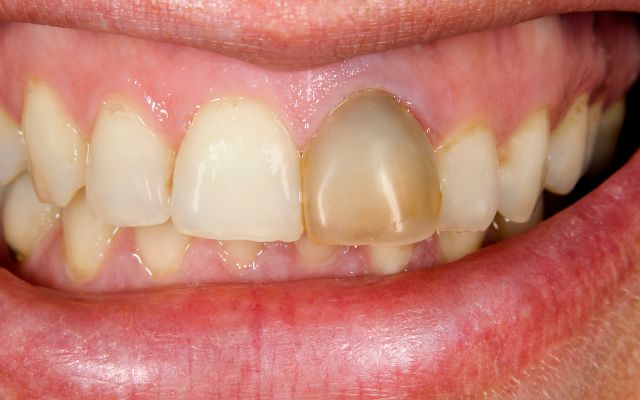
A dead tooth, sometimes referred to as a necrotic tooth, is a tooth that has lost its blood flow and nerve function. This can happen due to things like decay, injury, gum disease or other factors that harm the root of the tooth and cause it to die. This means the tooth can no longer get the nutrients it needs and can become discoloured and fragile, making it more susceptible to further damage and infections.
Causes of Dead Tooth
There are many factors can cause a dead tooth, including:
Decay or trauma
Decay is the result of bacteria and acids from plaque and tartar buildup eating away at a tooth. If left untreated, the decay can spread to the tooth’s innermost layer, the pulp, causing an infection and ultimately leading to the death of the tooth.
Trauma to the mouth, such as from a fall or a blow, can also cause a dead tooth by damaging the tooth’s nerves and blood vessels. In some instances, a tooth may die during a dental procedure, like a root canal or crown placement, if the pulp is harmed during the procedure.
Root canal failure
Root canal failure can result in a dead tooth for many reasons. When the pulpy inside of a tooth becomes infected or inflamed, a root canal procedure is performed to remove it and save the tooth. During the procedure, the infected or inflamed pulp is taken out and the inside of the tooth is cleaned and sealed.
But sometimes, the infection or inflammation can come back after the procedure, causing root canal failure. This can happen if the infected pulp wasn’t fully removed, the tooth got re-infected or there was a crack in the tooth that allowed bacteria to get back in.
The sealing material used during the root canal procedure can also deteriorate over time, letting bacteria in and causing an infection. This can also result in root canal failure and a dead tooth. In such cases, it may be necessary to remove the dead tooth and replace it with a dental implant or bridge.
Gum Disease
Periodontal disease—gum disease—is caused by plaque and tartar buildup along the gum line. Periodontal disease is gum disease. If left untreated, it can cause gum inflammation and infection, loosening the gums from the teeth. Over time, this can harm teeth-supporting bones and tissues and potentially induce dead tooth.
Gum disease can damage blood flow, resulting in a dead tooth. Infected gums and tissues around the tooth become inflamed. This constricts nearby blood vessels, reducing tooth blood supply. This can reduce the tooth’s oxygen and nutrition supply, killing the nerve and other components. Gum disease often exposes tooth roots, making them more vulnerable to harm or infection.
Advanced Age
Getting older can result in a decrease in blood flow to our teeth, which can lead to a dead tooth. As we age, the blood vessels and nerves in our pearly whites can become less efficient at supplying blood and oxygen to the pulpy bit inside the tooth, This contains the blood vessels and nerves. If the pulpy bit doesn’t get enough blood and oxygen, it can die, resulting in a dead tooth.
Older folk are also more likely to have underlying health issues, such as diabetes and heart problems, that can affect their oral health and increase the risk of problems like dead teeth.
What’s more, older folk may have had more dental work done over their lifetime, including root canal treatments, which can increase the chance of tooth death over time.
It’s important for people of all ages to look after their oral health by brushing and flossing regularly and seeing the dentist regularly to prevent oral health issues, including dead teeth.
Symptoms of A Dead Tooth

Several signs can indicate a dead tooth. Symptoms of a dead tooth include:
- Pain: Dead teeth can be quite painful, especially when biting down or applying pressure. This pain can range from a dull ache to sharp, stabbing sensations.
- Sensitivity: Dead teeth may be more sensitive to hot and cold temperatures, causing discomfort when eating or drinking.
- Discoloration: Dead teeth often become discolored and may appear yellow, gray or black in color.
- Swelling: The gums around a dead tooth may become swollen or tender.
- Drainage: In some cases, a dead tooth can cause a foul-smelling or tasteless discharge to occur.
- Tooth Mobility: Dead teeth may become loose or start to move, which can indicate that the underlying bone is also affected.
- Loose enamel: In the latter stages of a tooth’s demise, the supporting tissues may weaken and release the tooth from its socket. If not extracted by a dentist, the tooth may eventually fall out on its own. Additionally, dead teeth can cause poor breath and an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s vital to see a dentist straight away. The longer you leave a dead tooth untreated, the greater the risk it’ll cause further issues, like spreading infection or affecting neighboring teeth. In some situations, a dead tooth might need to be taken out and replaced with a dental implant or bridge.
Pain Management At Home
There are a few things you can do at home to alleviate tooth discomfort while you wait for treatment:
- Avoid hot beverages. They may cause inflammation, which might exacerbate your pain.
- Take a nonprescription anti-inflammatory medicine, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin).
- Avoid eating tough foods. Damaged nerves may be aggravated by the force of biting.
It is essential to visit the dentist immediately. Home remedies should not be substituted for professional medical care. Instead, you should utilize the following strategies as you wait for your appointment.
Dead Teeth Treatments

The treatment process for dead teeth typically involves three phases:
- Examination: During the first stage, the dentist will thoroughly examine your teeth and take x-rays or other diagnostic tests to determine the cause of the dead tooth and the extent of the damage.
- Treatment: Based on the examination results, the dentist will develop a treatment plan to save or remove the dead tooth. This could involve root canal therapy, extraction, dental implants, bridges, dentures, or gum surgery.
- Follow-up: After the treatment has been completed, the dentist will schedule a follow-up appointment to check on the healing process and ensure that the treated tooth is functioning properly. The dentist may also make recommendations for maintaining oral hygiene and preventing future problems.
It’s crucial to get dead teeth treated quickly smart to dodge any complications, like the spread of infection or knock-on effects on neighboring teeth. Your dentist can work out the top treatment choice for your individual needs and lead you through each step of the process.
Can You Prevent A Dead Tooth?
Yes, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing a dead tooth. Some of these include:
- Maintaining good oral hygiene.
- Visiting the dentist regularly.
- Eating a healthy diet.
- Put a mouthguard in your mouth. Always be sure to wear a mouthguard when engaging in a contact sport such as boxing or hockey so that you can protect your teeth from any potential damage.
- Avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Seeking prompt treatment for dental problems.
- Be sure to drink plenty of water, particularly after meals. In the time between brushings, drinking water might help remove bacteria from your teeth.
By taking these preventative steps, you can lower the chance of getting a dead tooth and keep your oral health in top shape.
Can a Dead Tooth Fall Out on Its Own?
No, a dead tooth won’t just fall out by itself. Over time, the tooth may become wobbly as the bones and tissues supporting it break down, but it won’t come out without a nudge. If you think you’ve got a dead tooth, it’s best to see a dentist as soon as you can.
Conclusion
To sum up, a dead tooth is a serious oral health concern that should not be ignored. The longer a dead tooth is left untreated, the more likely it is to cause additional problems, such as spread of infection or impact on surrounding teeth. If you suspect that you have a dead tooth, it’s important to seek treatment from a qualified dental professional as soon as possible.
At Spring Orchid Dental, we are committed to providing top-quality dental care and helping our patients maintain good oral health. If you’re experiencing symptoms of a dead tooth or if it’s time for your regular check-up, we invite you to book an appointment with us today. Our experienced dentists and friendly staff will provide you with personalized, compassionate care to help you achieve and maintain a healthy, beautiful smile.
FAQs
Do dead teeth need to be removed?
Yes, removing a dead tooth helps to prevent these potential complications and maintain good oral health. It’s important to find treatment for a dead tooth as soon as possible to ensure prompt and effective care.
What does a dead tooth feel like?
A dead tooth can cause several symptoms and sensations, such as:
- Pain or sensitivity
- Swelling or redness
- Darkening of the tooth
- Bad breath or taste
- Abscess formation
- Decay
Can a dead tooth make you sick?
Yes, a dead tooth left untreated can cause a bacterial infection. Then it will spread to other parts of your body, causing serious health issues.
While every treatment carries some risk of failure, root canal is usually a very successful treatment. It may last years if completed properly. Some cases are referred to specialists (Periodontists) to achieve the best outcome.
Please consult our professional team for more information on root canal treatments.
How long can a dead tooth stay in your mouth?
A dead tooth can remain in your mouth for a long time. Refusing to see the dentist for treatment can result in a variety of oral health issues and discomfort, hurting the appearance of your smile as well as your mental health.





