Why Do My Gums Bleed When I Brush My Teeth? Recurrent bleeding after brushing is usually caused by bronchitis, periodontitis, or other oral disorders.
Many individuals have bleeding gums while brushing their teeth, a dental condition that receives little attention since it is not serious. However, new studies suggest that frequent bleeding gums when brushing are a sign of poor oral health.
In this post, our Bassendean dentists will explain why your gums bleed when you brush.
Why Do My Gums Bleed When I Brush My Teeth?
Bronchitis, periodontitis, and other dental issues are the leading cause of recurrent bleeding after brushing. The Australian Dental Association recommends being checked out by a dentist as soon as possible if you notice any blood when cleaning your teeth.
Tartar, often called dental plaque, forms on unformed teeth because the environment is ideal for bacterial growth. Over time, this layer of plaque converges and sticks to the tooth surface, turning teeth yellow and triggering several significant dental problems such as gingivitis, bleeding gums, tooth decay, and halitosis.
Brushing or bleeding is a typical indicator we neglect. However, prolonged bleeding when brushing will cause numerous additional oral disorders that need immediate care. Possible teeth brushing or bleeding causes:
Dental Issues | Bodily Issues |
Too much brushing, horizontal brushing, or brushing too often might irritate and bleeding gums. Therefore, it’s important to scientifically and gently brush your teeth, use a circular motion, and clean every part of the oral cavity. The optimal time to clean your teeth is for 2 minutes, just before each meal, twice a day. Another reason for bleeding gums is picking at them with a toothpick instead of flossing, which scratches the gums and enlarges the holes where germs and food may get a foothold. |
Gum bleeding may also result from a lack of vitamin C or vitamin K. Vitamins like these aid in the coagulation process. If you notice your gums are bleeding, it’s a good idea to keep an eye on your diet and include extra vitamin C and vitamin K-rich foods. |
Brushing with hard toothbrush may cause damage to your gums due to its extreme hardness and the length and width of its bristles. Buy a soft-bristled toothbrush in the proper size for your mouth to prevent bleeding. Don’t use the wrong brush—try it and then change it if you feel it’s too hard. |
Diseases of the liver and bile might contribute to a situation in which the gums bleed easily. Gum bleeding is a common symptom of liver disease. |
Gingivitis may cause bleeding gums in periodontal disease because diseased gums are red, swollen, and sensitive. This problem is caused by tartar, a bacteria-filled plaque that sticks to teeth. However, tartar is hard to remove without professional dental equipment, so it’s best to contact the dentist. |
When brushing, hormonal changes in a woman’s body during adolescence, pregnancy, or menopause might cause bleeding gums. |
Toothache, decay, periodontal disease, and toothache cause bleeding gums during brushing. |
Antibiotics, for example, may cause vitamin K deficiency and gum bleeding if used over an extended period of time. Medications used to treat epilepsy and cancer might potentially trigger this side effect. |
Brushing your teeth may cause bleeding gums if you have dengue fever, leukemia, hemophilia, diabetes, etc., as well as if you are a heavy smoker, suffer from worry or stress related to your job or personal life, or have another medical condition that causes excessive bleeding.
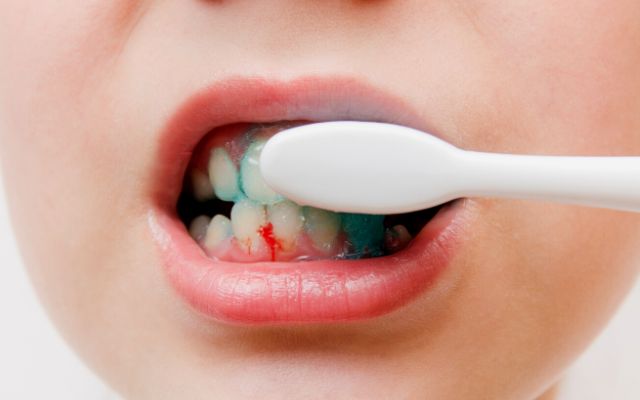
Is Bleeding Gums Dangerous?
If you often experience bleeding when brushing your teeth, it is imperative that you get medical attention. In the event that you have a little gum bleeding every once in a while, you need not panic; this condition often resolves itself within a few days. However, if this happens often, it is highly concerning since it may evolve into severe gingivitis and disrupt normal eating and everyday activities.
Bleeding gums while brushing teeth may progress to periodontitis, which can damage the teeth and surrounding tissues and potentially cause them to fall out. If left unchecked, this condition might endanger
- Cardiovascular illness with diabetes: Increases blood sugar and induces endocarditis, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Pregnant women: Increased chance of difficulties during pregnancy, resulting in early delivery and low birth weight kids.
At-Home Treatment to Stop The Bleeding Gums
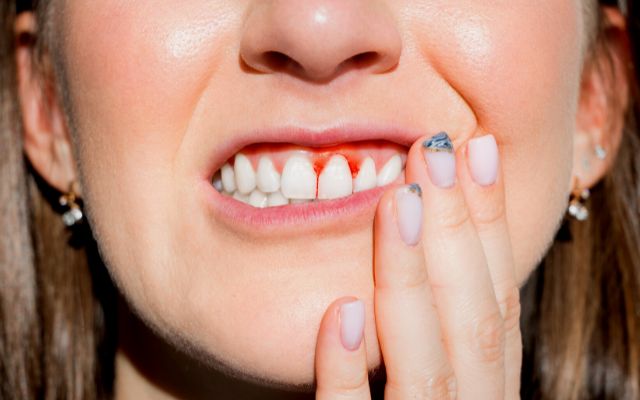

Our dentists at Spring Orchid Dental will guide you through 3 simple ways to stop the bleeding, lessen the swelling and discomfort in your gums, and prevent further episodes of bleeding:
Gauze Stops Bleeding
Applying a gauze promptly reduces bleeding and infection, whether it’s gums or an organ. Applying clean, wet gauze to bleeding gums stops the bleeding.
This procedure will assist normal individuals stop bleeding fast; if the hemostasis time is protracted and the volume of bleeding is significant, the reason may be coagulopathy or inadequate immunity. To halt the bleeding, the patient should visit Spring Orchid Dental Clinic.
Antibacterial Mouthwash
Patients with bleeding gums risk infection and persistent swelling and inflammation. Many forms of bacteria live in the mouth, thus patients with bleeding gums or other dental injuries should also use an antibacterial mouthwash.
Gargling with antibacterial water reduces inflammation, treats gingivitis, and prevents bleeding gums. Choose an antibacterial mouthwash with active components like hydrogen peroxide, and chlorhexidine,…
Cryotherapy
Cold compresses are better than gauze for halting the bleeding and lowering discomfort from severe gum injuries. Applying ice or cold compresses to the region where the gingivitis is bleeding can help you feel better soon.
Other Home Treatments For Bleeding Gums
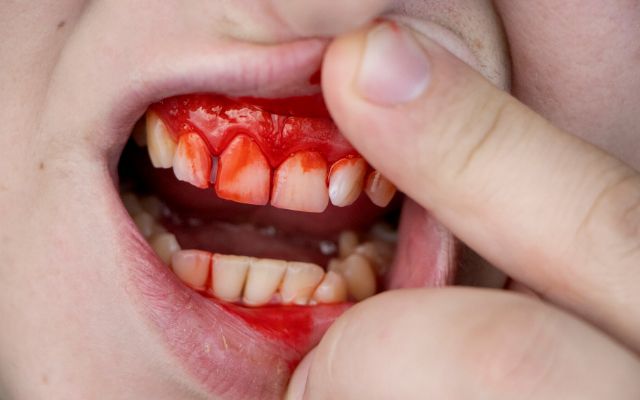
Too busy to make it to the dentist? No worries, our dentists at Spring Orchid Dental suggests the following home remedies for bleeding gums:
Saltwater
One of the simplest and most effective ways to cure mouth infections is to gargle with salt water. In addition to reducing swelling and discomfort, salt may also prevent further inflammation, cleanse the area, and destroy any hazardous germs present.
Instructions: Rinse your mouth several times a day with warm salt water with a 1:2 salt-to-water ratio or physiological saline with a 0.9% concentration to kill germs and reduce bleeding gums.
Note with Brushing and Bleeding Gums:
Continued and worsened bleeding gums when you brush may indicate numerous undelying issues:
- The bleeding tooth root may be more infected, enlarge, or produce pus, requiring lengthier therapy.
- Systemic disorders might also cause bleeding gums.
If gum bleeding persists, the patient should consult a dentist. Our dentists at Spring Orchid Dental will help you avoid bleeding gums by removing tartar, treating any gum disease and advising you on how to improve your diet and dental hygiene.
Our Spring Orchid Dental facility in Bassendean, Western Australia offers general dentistry treatments, including preventative and timely dental checkups.
FAQs
Which Illness Causes Frequent Gum Bleeding?
A warning symptom of type 1 or type 2 diabetes is persistent gum disease, including bleeding and swelling. Diabetics lack the immune system’s ability to fight against infections in the mouth. Because of this predisposition, the patient often has tooth and gum infections.
Why Can’t Gums Stop Bleeding?
Rickets may cause persistent gum bleeding. Additionally, vitamin K insufficiency may induce excessive bleeding of gums. Lack of vitamin K causes bleeding, especially bleeding gums, since it helps blood clot.
What To Eat To Stop Gum Bleeding?
Eat more vitamin K-rich foods like spinach, kale, lettuce, etc., to reduce the frequency of bleeding gums. Vitamin A deficiency, along with vitamins C and K, makes gums susceptible and bleed.





