How Long Can You Keep Your Teeth With Periodontal Disease? Untreated periodontitis may progress uncontrolled. Early periodontitis treatment, including expert dental care and good oral hygiene, is essential.
We’ll address that vital question in this post. There will be precise information regarding periodontal status, variables impacting tooth retention, and viable treatments to safeguard your teeth. Also, we will learn about the importance of regular dental care and oral self-care.
How Long Can You Keep Your Teeth With Periodontal Disease?


The amount of time a person with periodontal disease may preserve their teeth varies greatly. The severity of the condition, your dental health, your reaction to therapy, and your devotion to proper oral hygiene are all variables.
If periodontal disease is not treated, it may spread and destroy gum tissue, bone, and other tooth support components. At this time, tooth loss is a possibility. But, if you act fast and get good care, you may be able to stop or lessen the illness and keep your teeth for longer.
Finally, remember that periodontal disease is a chronic illness for which regular care is often necessary for good management. This involves frequent dental appointments for expert cleanings and check-ups and good oral hygiene at home.
Factors Affecting Tooth Retention in Periodontal Disease
There are many factors that affect the ability to retain teeth during periodontal disease. Here are some important factors:
- The severity of disease: Periodontal disease severity affects tooth retention. Early gingivitis and bacteria buildup may save teeth. However, when periodontal disease worsens, bone and tooth connective tissue loss loosens and threatens teeth.
- Individual Response: Everyone reacts differently to periodontal disease. Some individuals are better at controlling infections and restoring tooth connective tissue, while others are more prone to tooth loss.
- Oral hygiene and personal care: Periodontal disease requires good dental hygiene. You should brush twice a day, using dental floss or a joint cleaner, and using an antimicrobial mouthwash.
- Periodontal treatment: Maintaining teeth requires skilled periodontal disease treatment and management. Dental health requires treatment plan compliance and follow-up.
Overall, keeping teeth with periodontal disease relies on numerous aspects, including disease severity, individual response, dental hygiene and personal care, therapy and management, and general health. Most essential, get competent dental care, follow instructions, and get frequent exams to keep your teeth and mouth healthy.
What Occurs Without Periodontal Treatment?
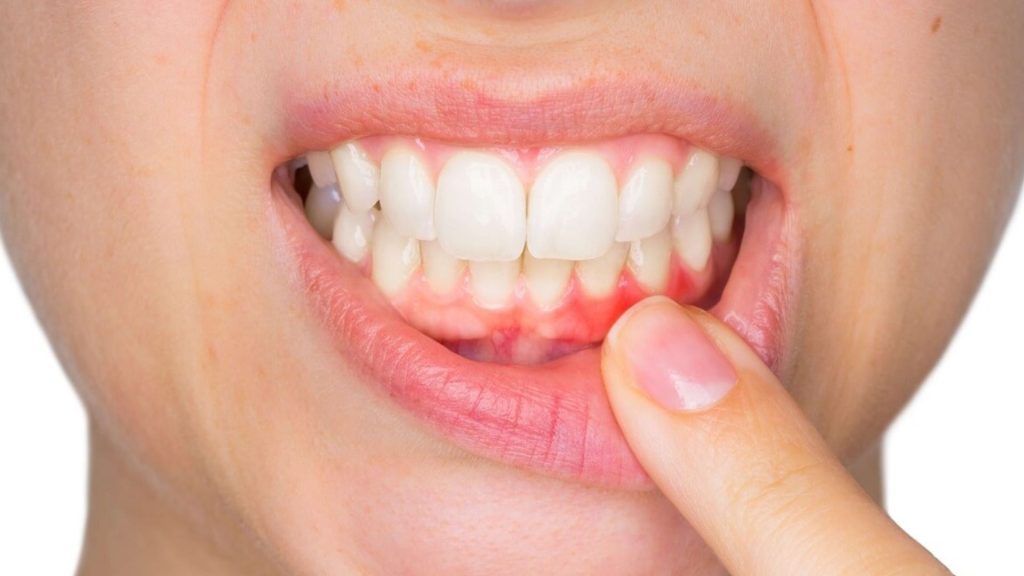

Periodontal disease will worsen without treatment, posing a significant threat to the health of your mouth and teeth. What may happen if periodontal disease isn’t treated:
- Tooth loss: Periodontal disease damages jawbone-tooth connective tissue. This connective tissue is damaged by periodontal disease and causes tooth loss.
- Recurrence and disease progression: Bacteria may develop untreated, causing irritation, recurrent gingivitis, and severe periodontal disease.
- Loss of bone tissue: It may induce jawbone bone loss, which weakens tooth structure. Loose teeth might fall out.
- Loss of jaw and aesthetics: The jaw and face might distort when teeth are removed owing to periodontal disease. Your looks and confidence may suffer.
- Overall health problems: Periodontal disease may cause heart disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, and stillbirth.
Thus, ignoring periodontal disease might harm your dental and general health. Maintaining healthy teeth and gums requires quick dental treatment and periodontal disease management.
Common Periodontal Disease Treatments
In order to manage and treat periodontal disease, a number of standard therapies are employed. Here is a rundown of all 3 most common procedures: professional cleaning, scaling, and root canal therapy.
Scaling & Root Planing
Only a dentist or dental specialist should attempt this.
Next, scaling removes plaque, bacterial plaque, and hard materials from the tooth surface and gums.
Then, the tooth surface and root are flattened to remove fissures and scars and allow new connective tissue to grow (root planing).
To clean and flatten properly, ultrasonic machines or scalers are typically needed.
Also, it’s painless and done under a dental anesthetic.
Gingivectomy And Periodontal Surgery
Some forms of periodontitis are so severe that more depth is required to remove the affected tissue.
Inflamed gum tissue and edema surrounding the teeth are removed during scaling.
Also, damaged bone tissue and microorganisms surrounding a tooth’s root are removed during root extraction.
Dental professionals execute this procedure.
After suturing, bone and gum tissue regenerate.
Treatment With Antibiotics
In serious infections, your dentist may prescribe medicines to destroy the germs.
However, antibiotics are just a temporary solution that is often paired with other therapies for the greatest results.
Most essential, consult and follow your dentist’s advice to pick the best periodontal disease therapy.
Routine Dental Checkups and Periodontal Care
Maintaining dental health requires periodontal maintenance. To maintain the efficiency and duration of periodontal therapy, frequent dental exams and post-treatment maintenance are crucial. Now, we’ll discuss post-periodontal illness dental checks and care advice in this part. This regular check-up and treatment will help manage periodontal disease and preserve your teeth:
Dental Checkups:
Keeping track of when you last had a dental examination is a crucial component of managing periodontal disease.
Appointments are normally every 3-6 months, depending on your periodontal status.
At your visit, your dentist will inspect your gums, bacteria levels, teeth, and mouth.
Treatment Aftercare:
The dentist will provide you with specific instructions and advice on how to care for your teeth and gums after periodontal disease treatment.
To eliminate plaque and germs, brush twice a day and use dental floss or a joint cleaning.
Using an antibacterial mouthwash following treatment may help keep your mouth clean and microorganisms under control.
Keep all planned follow-up visits so your doctor can monitor your progress and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
In general, dental examinations and follow-up care are crucial to preserving oral and dental health. So, following guidelines and seeing your dentist regularly can help you manage periodontal disease and keep your teeth and mouth healthy.
Conclusion


In this post, we discovered that “how long can you keep your teeth with periodontal disease?” depends on numerous circumstances. Maintaining good dental and oral health relies in large part on regular expert periodontal cleanings, treatments, and follow-ups. Also, the finest results may be achieved in treating periodontal disease with the help of a competent dental facility. Moreover, Periodontal disease treatment at Spring Orchid Dental Clinic is trustworthy.
Moreover, the dentists at Spring Orchid Dental Clinic are dedicated to delivering high-quality care, and they have the expertise and training to back it up. You’ll get expert dental treatment here!
FAQs
Can You Live A Long Life With Periodontal Disease?
If you have periodontal disease and get treatment, you can live a long and healthy life. Periodontal disease damages the gum tissue and supporting structures surrounding the teeth. The effects of periodontal disease on one’s everyday life and ability to eat and speak may be devastating if the condition is not addressed.
But, periodontal disease may be treated with regular dental treatment, including examinations and expert cleanings, and everyday oral care. This slows disease development and maintains oral health.
Is Periodontal Maintenance Forever?
No, it’s not. Periodontal disease is a chronic and potentially relapsing disease. However, with careful care and therapy, you may manage the condition and keep excellent dental health throughout life. Periodontal disease cannot be cured, but good treatment can manage and prevent it. However, illness therapy and management might alter over time and with your condition.
Therefore, frequent and thorough periodontal treatment is vital to promote dental health and avoid the recurrence of the illness, even if periodontal disease is not permanent.
How Rapidly Does Periodontitis Spread?
Periodontitis—advanced gum disease—progresses differently in each individual. Instead of spreading quickly, it grows slowly over months or years. However, many variables may affect advancement speed:
- Oral hygiene: Lack of brushing and flossing might hasten periodontitis. Bacteria grow in plaque, causing inflammation and tissue damage.
- Smoking: It reduces blood flow to the gums, lowers the immune system, and slows healing, making the illness worse.
- Genetic factors: Some people are genetically prone to severe periodontitis. Periodontitis may develop faster.
- Overall health: Diabetes and immunodeficiency problems may impair the body’s capacity to fight infections, especially gum infections. This accelerates periodontitis.
- Delayed treatment: Periodontitis might worsen if untreated. It may be slowed by early dental treatment and good oral hygiene.





