Bleeding gums are serious and should be addressed. Have you observed blood while brushing or flossing? You’re not alone. Many individuals encounter bleeding gums at some time in their life. Bleeding gums may seem like a small issue, but they may indicate an underlying issue that requires care. We think that information is power when it comes to oral health. We’ll study bleeding gums, reveal the secrets of optimum oral care, and empower you to take charge of your dental health. Let’s find excellent bleeding gum treatments together:
Bleeding Gums: Causes and Associated Conditions
Based on Webmd, bleeding gums can be a worrisome sign that something else is wrong with your mouth health. For successful treatment, it is essential to first identify the root causes of bleeding gums. This article will discuss the numerous disorders and factors that might lead to this issuse. By understanding these variables, you may avoid gum disease and maintain healthy gums:
Gingivitis
It is one of the most common causes of bleeding gums. Gingivitis happens when plaque, a sticky film of germs, builds up on the teeth and gums. The bacteria in plaque release toxins that hurt the gums, causing them to swell and bleed. If you don’t treat gingivitis, it can lead to periodontitis, a more serious form of gum disease.
Periodontitis
It is a serious form of gum disease that affects the muscles and bones that hold the teeth in place. Periodontitis may cause bleeding gums, tooth loss, gum recession, and bone deterioration. Bacteria develop in deep pockets between the gums and teeth, worsening the illness. Managing periodontitis and stopping it from getting worse requires good mouth care and professional treatment.
Diabetes
People with untreated diabetes are more likely to get gum disease and swollen gums as a result. High blood sugar levels can weaken the immune system, cut off blood flow to the gums, and slow the recovery process. Diabetic people must keep their blood sugar under control and get regular dental care to avoid gum problems.
Leukemia
Because there are fewer platelets in the blood, bleeding gums can be a sign of leukemia. Platelets stop bleeding. Patients with leukemia who have a low platelet count can easily get bruises, nosebleeds, and swollen gums. Diagnosis and treatment need early medical intervention.
Thrombocytopenia
A low number of platelets in the blood is a sign of thrombocytopenia. Reduced platelets can cause bleeding gums, just like leukemia can. It may be caused by drugs, viruses, autoimmune diseases, or bone marrow problems. The best way to treat thrombocytopenia is to treat the root reason and, in some cases, give platelet transplants.
Hemophilia or von Willebrand Disease
It is caused by a lack of clotting factors, while von Willebrand disease is caused by a lack of or problem with von Willebrand factor, a protein that is needed for blood to form properly. Both disorders may cause bleeding gums, nosebleeds, and easy bruising. Specialists treat these bleeding problems.
Vitamin Deficiencies
Certain vitamins might cause your gums to bleed if you don’t receive enough of them. A deficiency of vitamin C may cause blood vessels to weaken and bleed more easily. Scurvy is an infection that causes gums to enlarge and bleed, among other things. Also, gum bleeding may result from a vitamin K deficiency, which helps blood clot. A balanced diet and vitamin-rich meals are essential for healthy gums.
Brushing & Flossing Technique
Have you ever wondered why do your gums bleed when you brush your teeth? If you brush too hard or use a hard-bristled toothbrush, your gums can get sore and bleed. The best way to clean your teeth and gums is with a soft bristles toothbrush and gentle, circular strokes. Also, bleeding gums might result from poor flossing. Avoiding the discomfort and bleeding that might result from flossing is worth the effort. Use a sawing motion that is soft enough for sensitive gums and curl the floss around each tooth to clean below the gumline.
Gums and Canker Sores
Canker sores, commonly known as mouth ulcers, may cause irritation in the gums. These are the tiny, superficial sores that might cause bleeding when you brush or bite on anything. Although stress, hormonal changes, and even certain foods may have a role, the precise origin of canker sores is unclear. Using a light, alcohol-free mouthwash and avoiding hot or acidic foods can help ease symptoms.
How to Stop Bleeding Gums at Home?
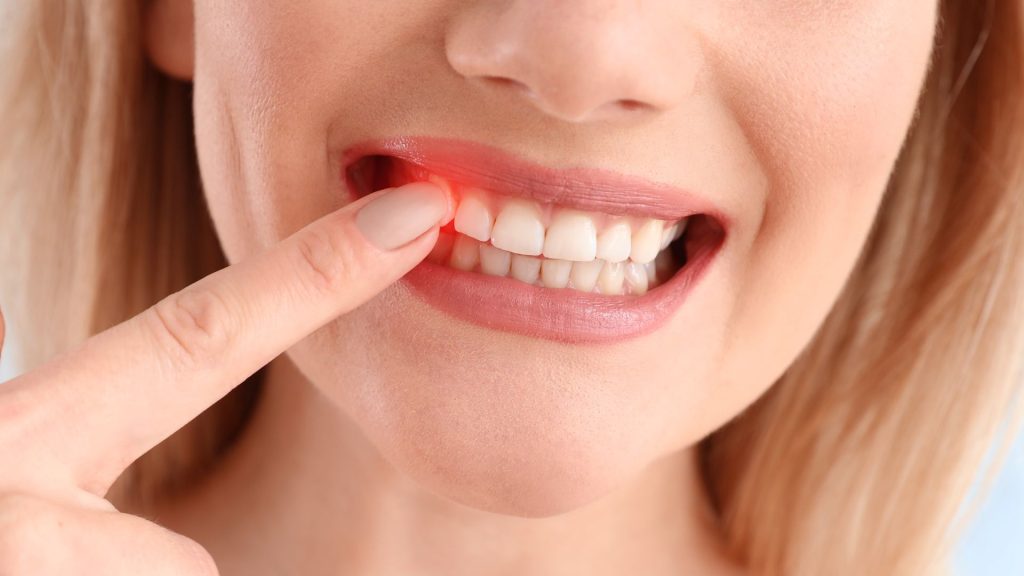

If your gums bleed, it’s critical that you take adequate care of them at home as part of your oral health regimen. This section will discuss critical home care measures that may help avoid gum swelling and other concerns. Following these methods and concentrating on dental care may improve gum health:
Proper Brushing Technique
Keeping your gums healthy requires that you brush in the right way. Follow these steps to brush properly:
- Soft-bristled toothbrush: Avoid gum irritation with a soft-bristled toothbrush.
- Hold the toothbrush 45 degrees toward the gum line.
- Clean your teeth with gentle circular strokes. Focus on the gum line, where plaque accumulates.
- Then, brush your teeth chewing surfaces back and forth.
- Next, brushing your tongue gently removes microorganisms and freshens your breath.
- Brush your teeth twice a day, ideally in the morning and before night.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
The condition of your gums might be affected by your way of living. Take into account the following:
- Balanced diet: Include fruits, vegetables, entire grains, and lean meats. Citrus, berries, and leafy greens contain gum-healthy vitamin C.
- Sugary meals and drinks may cause plaque accumulation and gum disease. Limit sugary snacks, drinks, and juices.
- Smoking stains teeth impairs the immune system, and slows gum repair. Also, smoking may damage gums.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress weakens your immune system and increases gum disease risk. To reduce stress, exercise, meditate, or do hobbies.
When to Seek Professional Help?
Bleeding gums may be managed at home, but sometimes professional aid is needed. Recognizing expert intervention indicators helps avoid problems and guarantee effective treatment. This section discusses when bleeding gums need dental treatment.
- Persistent or Excessive Bleeding: If your gums bleed after a week of good home treatment, you need expert assistance. A dentist can identify and treat persistent or severe bleeding, which may indicate gum disease or other oral health concerns.
- Severe Pain or Discomfort: Mild discomfort or sensitivity during early gum disease or moderate gum irritation is normal, but severe pain or chronic discomfort should not be disregarded.
- Swollen or Inflamed Gums: If your gums look swollen, red, or irritated, you may have an infection or inflammation in your gums. These symptoms may indicate gingivitis or periodontitis, which needs medical attention.
- Receding Gums or Loose Teeth: If your gums are retreating or your teeth feel loose or insecure, this could be a sign of severe gum disease. Receding lips and loose teeth are important problems that should be fixed right away by a dentist.
Diagnosis and Treatment Plan
The dentist will provide a diagnosis and explain the treatment plan based on the results of the examination. The precise reason for your bleeding gums will determine the course of therapy, which may include the following.
- Scaling and root planing: The dentist may suggest root planing and scaling to remove plaque and tartar from the root surfaces of the teeth and gums if gum disease is present.
- Antibacterial mouthwash: Gum irritation and bacterial overgrowth may be mitigated with the use of an antimicrobial mouthwash.
- Medications: To treat gum infections or other medical disorders that cause bleeding gums, the dentist may prescribe antibiotics.
- Oral hygiene instructions: The dentist will provide you with personalized brushing and flossing recommendations. They may prescribe a soft-bristled toothbrush, gentle circular movements, and floss or interdental brushes.
In conclusion, a dentist’s office visit for bleeding gums entails a complete evaluation, diagnosis, and customized treatment plan. You can cure bleeding gums and address the reasons by obtaining expert care. To avoid future problems, follow the dentist’s advice, attend follow-up visits, and practice proper dental hygiene.
Conclusion

Bleeding gums can be a sign of major problems like gingivitis or periodontal disease, so don’t ignore them. Complications such as gum swelling, tooth loss, and bone injury may be avoided with early identification and rapid treatment. Therefore, we recommend frequent dental checkups to preserve oral health and avoid complications. Also, we provide excellent and courteous service at Spring Orchid Dental facility.
In addition, frequent dental checkups enable your dentist to teach you how to care for your mouth every day. To keep your gums and teeth healthy, your dentist will teach you brushing, flossing, and healthy living.
FAQs
What Happens If You Ignore Bleeding Gums?
Neglecting bleeding gums might harm your dental health. If you ignore bleeding gums, several issues may arise:
- Progression of gum disease: Untreated gum disease may develop to periodontitis. As the condition progresses, gums recede, creating pockets around teeth that encourage bacterial development and infection. Tooth loss and bone injury may ensue.
- Gum infections and abscesses: Bacterial growth may cause gum infections and abscesses with swelling, discomfort, and pus-filled pockets. These painful infections may need medications or drainage.
- Tooth decay and cavities: Tooth loss and cavities can also happen more often if your gums bleed. Bacteria near the gum line and in pockets may cause cavities by breaking down tooth enamel. Inflamed gums may retreat, exposing tooth roots and increasing decay risk.
Thus, bleeding gums are not natural and should not be disregarded. Early action and good dental hygiene may save your smile and health.
Should You Brush Your Gums If They Bleed?
Yes, you should. Brush your teeth, including your gums, even if they’re bleeding. While oral hygiene is vital, if your gums bleed after moderate brushing and flossing, you should consult a dentist. A dentist can assess your dental health, determine the reason for the bleeding gums, and provide effective therapy. Remember, excellent dental hygiene and expert treatment may support healthy gums and avoid issues.
Why Is Your Gum Bleeding No Pain?
When your gums bleed without hurting, it can be worrying because it may seem strange or contradicting. Bleeding gums are serious, even if there’s no pain. Bleeding gums without pain may indicate a problem. So, consult a dentist to establish the source of your bleeding gums and obtain treatment and oral health advice.





